The functionality of starters and alternators have improved and evolved since their introductions in 1912 and 1960. In the decades since then, higher compression ratios, increased accessory electrical loads, and the move toward hybridization and emissions compliance have brought many changes to the design and requirements of these rotating electrical components.
Charles Kettering is credited with the original electric self-starter motor, as used in the 1912 Cadillac Model 30. This landmark invention was more than just a means of eliminating the hand-crank method of starting the family car, it was the heart of the first complete automotive electrical system. The Kettering starter was actually a starter-generator, providing accessory power for lights, horn, and also recharging a bank of four six-volt batteries. Most early electrical systems would be 6-volt DC until the 1950’s, when 12 volts became standard. The Cadillac’s starter required 24V, but the rest of the electrical system was a 6V design.
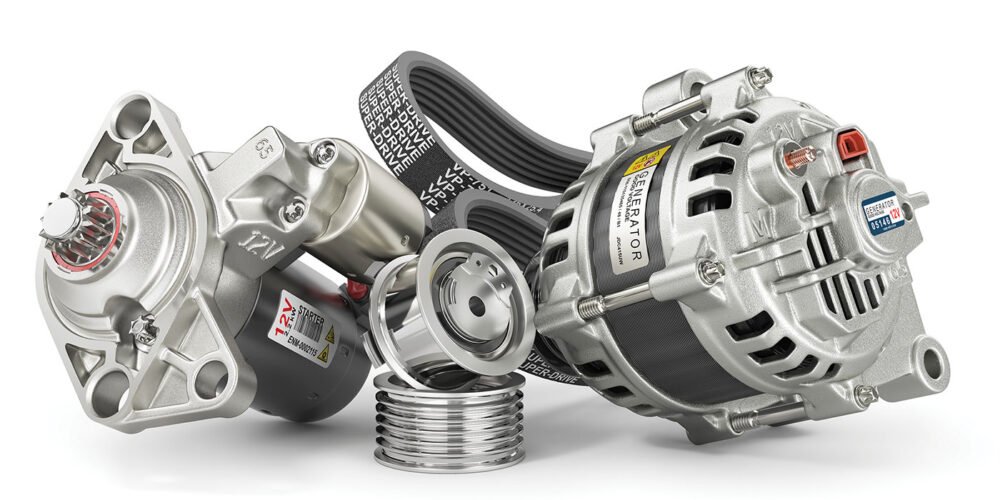
Today’s starter motors are largely of the permanent magnet gear reduction (PMGR) type, a compact design that uses a series of internal gears to create greater torque at the flywheel. Gear reduction allows for a smaller motor to create high torque with lower energy being drawn from the battery, with benefits of space, weight savings, and electrical efficiency. Previous starters were of the “direct-drive” type, with the pinion gear attached directly to the armature shaft of the motor. The PMGR starter armature rotates about 4X faster than its pinion gear, while direct-drive is a 1:1 ratio. As a result, direct-drive starters are larger, heavier, and less efficient. They are also more prone to overheating during extended cranking. Kettering’s starter motor was of the direct-drive design, but connected to an external gear reduction system to increase torque output to the flywheel.
Early direct-drive starters also feature a pinion engagement mechanism often known as the “Bendix,” named for its inventor, Vincent Bendix. (Vincent was also a pioneer in the automotive and aviation brake industries). A spring-loaded gear sliding along the armature shaft “kicks out” to engage the flywheel ring gear and crank the engine over when the starter is engaged. Modern starters (PMGR and direct-drive alike) use a solenoid and one-way overrunning clutch to move the pinion gear into position, but many veteran techs and parts specialists still call the starter drive gear a “Bendix.”
Most parts specialists are already familiar with another overrunning clutch, found in the pulleys of many modern alternators. Overrunning alternator pulleys (OAPs) and overrunning alternator decouplers (OADs) allow the alternator to freewheel upon engine shutdown, while OADs also have a torsion spring to dampen engine pulses and optimize belt drive performance. OAD/OAP assemblies are the latest innovation in alternator technology that began during WWII, and entered the automotive world with the Plymouth Valiant in 1960.
Prior to the Valiant, most automobiles used a DC generator to provide power for the accessory and charging systems. Like direct-drive starters, these units were bulky, heavy, and inefficient. Generators produced relatively low amperage (12A-60A), were coupled with crude voltage regulators, and often overcharged the batteries they fed. Alternators entered the market after most vehicles had already switched to the now-familiar 12V DC electrical system. Early alternators also relied on an external voltage regulator, with GM transitioning to internally-regulated (IR) alternators in the 1970’s, Ford in the early 1980’s, and Chrysler keeping external regulators into the 1990’s for vehicles that did not incorporate voltage regulation into the PCM circuitry.
Modern alternators are commonly identified by their output in amperes. The “amp rating” and original manufacturer are often used to select the correct alternator in catalogue prompts, but is difficult to determine without examining the alternator itself, or without dealership assistance. Since very few alternator tags can been viewed with the component in place, it remains a challenge. This amp rating refers to the maximum amperage output achievable, and depends on the RPM of the input shaft. The actual output of any alternator is dependent on the electrical load required at any given moment. While an under-rated alternator may never achieve enough amperage to support the loads required, a “high-output” alternator may never be asked by the charging system to provide its maximum potential amperage!
Just as Charles Kettering envisioned a system for Cadillac more than 100 years ago, the starter-generator is making a comeback with hybrid and mild hybrid vehicles today. Belt-driven or integrated with other components (engine, transmission, or differential), starter-generators can be used in tandem with an internal combustion engine or as a standalone electric drive source. And much like Kettering’s dual 6/24V charging and starting system, these modern hybrid designs use a combination of 12 and 48V circuits to provide power for starting, charging, and accessory needs.